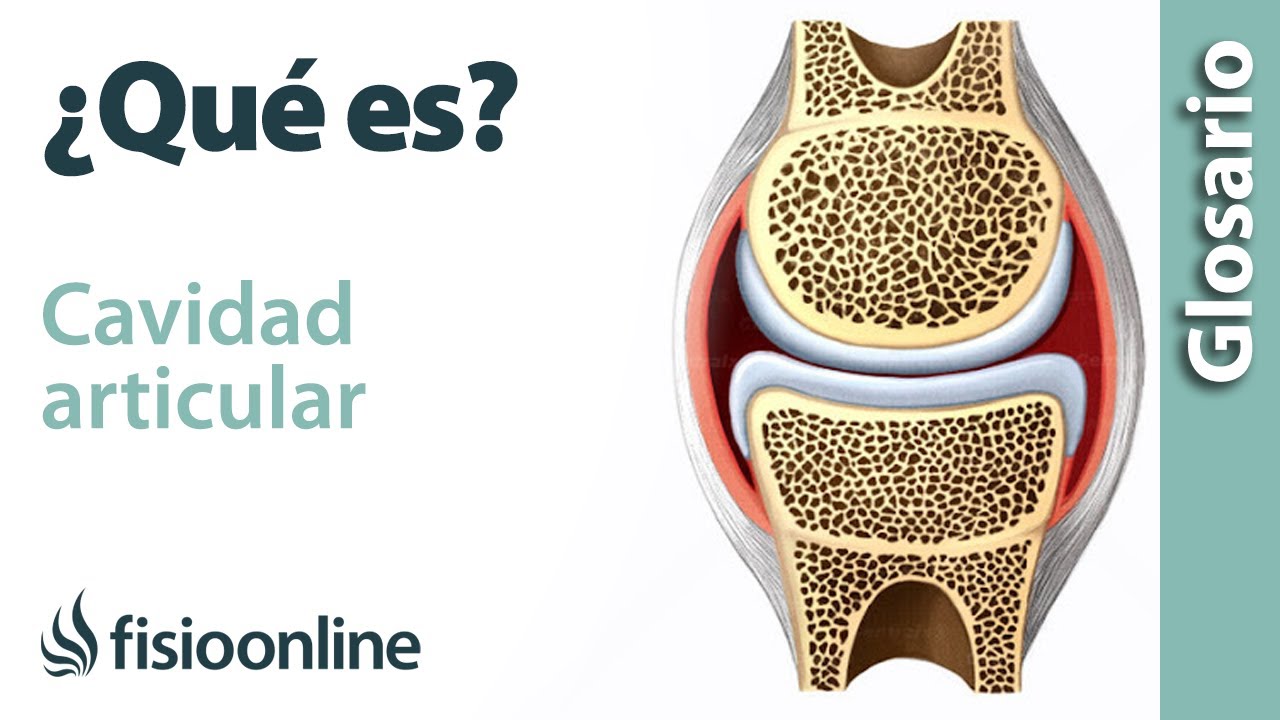
Which joints have synovial fluid? Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage.
Synovial fluid is produced by the synovial membrane, which lines the joint cavity. It contains hyaluronic acid, which gives the fluid its viscous consistency, and proteins, which provide lubrication and nourishment to the articular cartilage.
Synovial fluid is essential for joint health. It helps to reduce friction between the bones, cushions the joint, and provides nutrients to the articular cartilage. Without synovial fluid, the joints would be stiff and painful.
Most synovial joints are freely movable. They include the:
- Shoulder joint
- Elbow joint
- Wrist joint
- Hip joint
- Knee joint
- Ankle joint
Joints That Have Synovial Fluid
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
- Lubrication: Synovial fluid reduces friction between the bones during movement.
- Cushioning: Synovial fluid helps to cushion the joint and protect it from impact.
- Nutrition: Synovial fluid provides nutrients to the articular cartilage, which is a thin layer of tissue that covers the ends of the bones.
- Waste removal: Synovial fluid helps to remove waste products from the joint.
- Temperature regulation: Synovial fluid helps to regulate the temperature of the joint.
- Immune function: Synovial fluid contains immune cells that help to protect the joint from infection.
- Joint stability: Synovial fluid helps to stabilize the joint and prevent dislocation.
Synovial fluid is essential for joint health. Without it, the joints would be stiff and painful. Synovial fluid is produced by the synovial membrane, which lines the joint cavity. The synovial membrane is a thin layer of tissue that contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
Lubrication
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the most important functions of synovial fluid is to lubricate the joint. It does this by reducing friction between the bones during movement. This is essential for joint health, as friction can cause wear and tear on the articular cartilage. Without synovial fluid, the joints would be stiff and painful.
The lubrication provided by synovial fluid is also important for proprioception, which is the body's ability to sense the position of its joints. Proprioception is essential for coordination and balance.
In summary, synovial fluid is essential for joint health. It lubricates the joint, reduces friction, and provides nutrients to the articular cartilage. Without synovial fluid, the joints would be stiff and painful.
Cushioning
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the most important functions of synovial fluid is to cushion the joint and protect it from impact. It does this by absorbing shock and distributing it evenly throughout the joint. This is essential for joint health, as impact can damage the articular cartilage and other joint structures.
For example, when you jump or run, the synovial fluid in your knee joint helps to absorb the impact and protect your knee from injury. Without synovial fluid, your knee joint would be much more likely to be damaged by impact.
In summary, synovial fluid is essential for joint health. It lubricates the joint, reduces friction, cushions the joint, and provides nutrients to the articular cartilage. Without synovial fluid, the joints would be stiff, painful, and more likely to be injured.
Nutrition
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the most important functions of synovial fluid is to provide nutrients to the articular cartilage. Articular cartilage is a thin layer of tissue that covers the ends of the bones. It is made up of specialized cells called chondrocytes, which are responsible for producing and maintaining the cartilage matrix.
The cartilage matrix is made up of collagen, proteoglycans, and water. Collagen gives the cartilage its strength and flexibility, while proteoglycans attract and hold water, giving the cartilage itsing properties. Water makes up about 70% of the cartilage matrix and is essential for its proper function.
Synovial fluid provides nutrients to the articular cartilage by diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The synovial fluid is rich in nutrients, such as glucose, oxygen, and amino acids. These nutrients diffuse into the articular cartilage and are used by the chondrocytes to produce and maintain the cartilage matrix.
Without synovial fluid, the articular cartilage would not be able to receive the nutrients it needs to function properly. This would lead to a breakdown of the cartilage and eventually to osteoarthritis.
- Facet 1: The role of synovial fluid in nourishing the articular cartilage
Synovial fluid provides nutrients to the articular cartilage by diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The synovial fluid is rich in nutrients, such as glucose, oxygen, and amino acids. These nutrients diffuse into the articular cartilage and are used by the chondrocytes to produce and maintain the cartilage matrix.
- Facet 2: The importance of articular cartilage
Articular cartilage is a thin layer of tissue that covers the ends of the bones. It is made up of specialized cells called chondrocytes, which are responsible for producing and maintaining the cartilage matrix. The cartilage matrix is made up of collagen, proteoglycans, and water. Collagen gives the cartilage its strength and flexibility, while proteoglycans attract and hold water, giving the cartilage its cushioning properties. Water makes up about 70% of the cartilage matrix and is essential for its proper function.
- Facet 3: The consequences of synovial fluid deficiency
Without synovial fluid, the articular cartilage would not be able to receive the nutrients it needs to function properly. This would lead to a breakdown of the cartilage and eventually to osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that is characterized by pain, stiffness, and swelling. It is the most common type of arthritis and is a major cause of disability.
- Facet 4: The importance of maintaining healthy synovial fluid
Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for joint health. There are a number of things that you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Getting enough sleep
By following these tips, you can help to maintain healthy synovial fluid and protect your joints from damage.
Waste removal
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the important functions of synovial fluid is to remove waste products from the joint. Waste products are produced by the cells in the joint as a byproduct of metabolism. If these waste products are not removed, they can build up and damage the joint.
- Facet 1: The role of synovial fluid in waste removal
Synovial fluid helps to remove waste products from the joint by flushing them out. The synovial fluid is constantly circulating, and as it circulates, it picks up waste products and carries them away from the joint.
- Facet 2: The importance of waste removal
Removing waste products from the joint is essential for joint health. If waste products are not removed, they can build up and damage the joint. This can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Facet 3: The consequences of synovial fluid deficiency
If the synovial fluid is not able to remove waste products from the joint, it can lead to a build-up of waste products and damage to the joint. This can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Facet 4: Maintaining healthy synovial fluid
Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for joint health. There are a number of things that you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Getting enough sleep
By following these tips, you can help to maintain healthy synovial fluid and protect your joints from damage.
Temperature regulation
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the important functions of synovial fluid is to help regulate the temperature of the joint. This is important because the joint needs to be at a certain temperature in order to function properly.
- Facet 1: The role of synovial fluid in temperature regulation
Synovial fluid helps to regulate the temperature of the joint by absorbing heat and releasing it as needed.
- Facet 2: The importance of temperature regulation
Maintaining a proper temperature is essential for joint health. If the joint is too cold, it can become stiff and painful. If the joint is too hot, it can lead to inflammation and damage to the joint tissues.
- Facet 3: The consequences of synovial fluid deficiency
If the synovial fluid is not able to regulate the temperature of the joint, it can lead to problems such as stiffness, pain, inflammation, and damage to the joint tissues.
- Facet 4: Maintaining healthy synovial fluid
Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for joint health. There are a number of things that you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Getting enough sleep
By following these tips, you can help to maintain healthy synovial fluid and protect your joints from damage.
Immune function
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the important functions of synovial fluid is to protect the joint from infection. Synovial fluid contains immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, which help to fight off bacteria and other microorganisms that may enter the joint.
- Facet 1: The role of immune cells in synovial fluid
Immune cells in synovial fluid play a vital role in protecting the joint from infection. Macrophages are large, phagocytic cells that engulf and destroy bacteria and other foreign particles. Neutrophils are white blood cells that are attracted to the site of infection and release chemicals that kill bacteria.
- Facet 2: The importance of synovial fluid in joint health
Synovial fluid is essential for joint health. It provides lubrication, cushioning, and nourishment to the joint. It also helps to remove waste products from the joint and regulate the temperature of the joint. Without synovial fluid, the joint would be stiff and painful and more susceptible to infection.
- Facet 3: The consequences of synovial fluid deficiency
Synovial fluid deficiency can lead to a number of problems, including joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. It can also increase the risk of infection. Synovial fluid deficiency can be caused by a number of factors, including injury, inflammation, and certain medical conditions.
- Facet 4: Maintaining healthy synovial fluid
Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for joint health. There are a number of things that you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Getting enough sleep
By following these tips, you can help to maintain healthy synovial fluid and protect your joints from infection.
Joint stability
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
One of the important functions of synovial fluid is to help stabilize the joint and prevent dislocation. Synovial fluid does this by filling the joint cavity and creating a seal between the bones. This seal helps to prevent the bones from moving out of place.
- Facet 1: The role of synovial fluid in joint stability
Synovial fluid helps to stabilize the joint by filling the joint cavity and creating a seal between the bones. This seal helps to prevent the bones from moving out of place.
- Facet 2: The importance of joint stability
Joint stability is essential for normal movement. Without joint stability, the bones would be able to move out of place, which could lead to pain, instability, and injury.
- Facet 3: The consequences of synovial fluid deficiency
Synovial fluid deficiency can lead to joint instability. Joint instability can occur when the synovial fluid is not able to fill the joint cavity and create a seal between the bones. This can lead to pain, instability, and injury.
- Facet 4: Maintaining healthy synovial fluid
Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for joint stability. There are a number of things that you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including:
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding smoking
- Getting enough sleep
By following these tips, you can help to maintain healthy synovial fluid and protect your joints from instability.
FAQs about Synovial Fluid
Synovial fluid is a viscous, egg-white-like fluid that fills the joint cavity and nourishes the articular cartilage. It is found in freely movable joints, such as the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle joints.
Question 1: What are the functions of synovial fluid?
Answer: Synovial fluid has a number of important functions, including lubrication, cushioning, nourishment, waste removal, temperature regulation, immune function, and joint stability.
Question 2: What happens if I have synovial fluid deficiency?
Answer: Synovial fluid deficiency can lead to a number of problems, including joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and instability. It can also increase the risk of infection.
Question 3: How can I maintain healthy synovial fluid?
Answer: There are a number of things you can do to help maintain healthy synovial fluid, including exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and getting enough sleep.
Question 4: What are the symptoms of synovial fluid problems?
Answer: The symptoms of synovial fluid problems can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and instability.
Question 5: How is synovial fluid deficiency diagnosed?
Answer: Synovial fluid deficiency is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination and a review of the patient's symptoms. In some cases, imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Question 6: How is synovial fluid deficiency treated?
Answer: The treatment for synovial fluid deficiency depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may involve lifestyle changes, such as exercise and weight loss. In other cases, medication or surgery may be necessary.
Summary: Synovial fluid is an important fluid that plays a vital role in joint health. Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for preventing joint problems.
Transition to the next article section: For more information about synovial fluid and joint health, please consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Synovial fluid is a vital component of healthy joints. It provides lubrication, cushioning, nourishment, waste removal, temperature regulation, immune function, and joint stability. Maintaining healthy synovial fluid is essential for preventing joint problems.
If you are experiencing joint pain, stiffness, swelling, or instability, it is important to see a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment of synovial fluid problems can help to prevent further damage to the joint.
Discover Glance Intuit: The Ultimate Remote Access Solution
74 Examples Of Organic And Inorganic Compounds | Ultimate Guide
Common Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System Disorders
CAVIDAD ARTICULAR Qué es, ubicación, función y lesiones YouTube

Líquido Sinovial ¿Qué es y para que sirve? Clinica Fixen

¿Cuál es la función del líquido sinovial? Curiosoando