What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
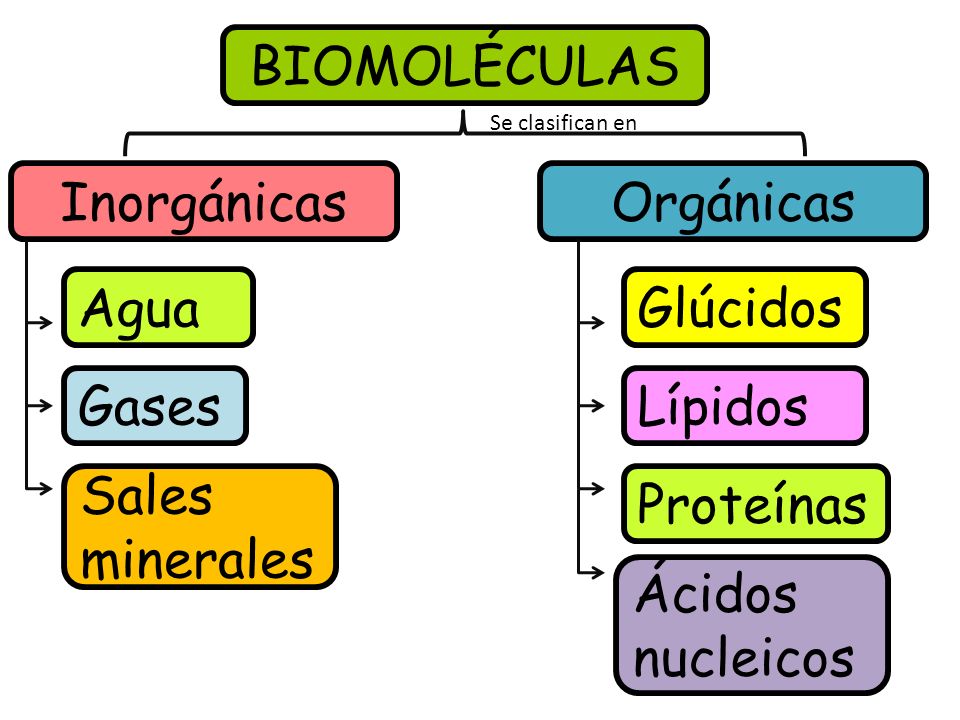
Organic molecules are chemical compounds that contain carbon. They are the building blocks of all living things, and they include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Inorganic molecules do not contain carbon. They include water, salt, and minerals.
Organic molecules are typically more complex than inorganic molecules, and they can form a wider variety of shapes and structures. They are also more reactive than inorganic molecules, which means that they are more likely to participate in chemical reactions.
The distinction between organic and inorganic molecules is important because it helps us to understand the different properties of these two types of compounds. Organic molecules are essential for life, while inorganic molecules are essential for the environment. Both types of molecules play an important role in the world around us.
Here are some examples of organic and inorganic molecules:
- Organic molecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
- Inorganic molecules: water, salt, minerals
Organic molecules are found in all living things, while inorganic molecules are found in both living and non-living things.
Concepto de Moleculas Organicas e Inorganicas
Organic and inorganic molecules are two broad classes of chemical compounds that differ in their composition and properties. Organic molecules are compounds that contain carbon, while inorganic molecules do not.
- Composition: Organic molecules contain carbon, while inorganic molecules do not.
- Structure: Organic molecules are typically more complex and have a wider variety of shapes and structures than inorganic molecules.
- Reactivity: Organic molecules are typically more reactive than inorganic molecules.
- Solubility: Organic molecules are typically less soluble in water than inorganic molecules.
- Occurrence: Organic molecules are found in all living things, while inorganic molecules are found in both living and non-living things.
- Importance: Organic molecules are essential for life, while inorganic molecules are essential for the environment.
The distinction between organic and inorganic molecules is important because it helps us to understand the different properties of these two types of compounds. Organic molecules are essential for life, while inorganic molecules are essential for the environment. Both types of molecules play an important role in the world around us.
Composition
This distinction is fundamental to the concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas. Carbon is a unique element with the ability to form covalent bonds with itself and with other elements, giving rise to a vast array of organic molecules with diverse structures and properties.
- Facet 1: The Role of Carbon
Carbon's ability to form stable covalent bonds with itself and other elements allows for the formation of complex and diverse organic molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These molecules are the building blocks of life and are essential for all living organisms.
- Facet 2: Examples of Organic and Inorganic Molecules
Organic molecules include glucose (a sugar), ethanol (an alcohol), and methane (a hydrocarbon). Inorganic molecules include water, carbon dioxide, and sodium chloride (table salt). These examples illustrate the diverse range of organic and inorganic molecules and their varying compositions.
- Facet 3: Implications for Life
The unique properties of organic molecules make them essential for life. Their ability to form complex structures and their reactivity allow them to participate in the intricate chemical reactions that occur within living organisms.
- Facet 4: The Importance of Inorganic Molecules
While organic molecules are essential for life, inorganic molecules also play crucial roles. Water, for example, is essential for all living organisms and is involved in many biological processes. Inorganic molecules also provide essential nutrients, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium.
In summary, the distinction between organic and inorganic molecules based on their composition is fundamental to understanding their diverse roles and importance in the world around us.
Structure
This aspect of concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas is crucial because the structure of a molecule determines its properties and functions. Organic molecules, with their intricate and diverse structures, exhibit a vast array of properties, enabling them to perform a wide range of biological and chemical functions.
The complexity and structural diversity of organic molecules arise from the unique properties of carbon. Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with each other and with other elements, giving rise to a multitude of possible molecular arrangements. This versatility allows for the formation of complex structures, including linear chains, branched chains, rings, and three-dimensional shapes.
In contrast, inorganic molecules tend to have simpler structures. They are often composed of ions arranged in regular patterns, resulting in crystalline or symmetrical structures. The simplicity of inorganic molecule structures limits their diversity and range of properties compared to organic molecules.
The structural complexity of organic molecules is essential for life. The intricate shapes and functional groups of organic molecules enable them to interact with each other and with other molecules in highly specific ways. This specificity is critical for biological processes such as enzyme catalysis, protein folding, and molecular recognition.
Understanding the relationship between the structure and function of organic molecules is crucial for fields such as biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. By studying the structures of organic molecules, scientists can gain insights into their biological activities and design new molecules with desired properties.
Reactivity
This aspect of concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas is significant because reactivity governs the ability of molecules to undergo chemical reactions and transformations. The higher reactivity of organic molecules stems from the unique properties of carbon and the presence of functional groups.
Carbon atoms have the ability to form covalent bonds with a variety of other elements, including hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and halogens. These bonds can be single, double, or triple, giving rise to a diverse range of functional groups. Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that confer characteristic chemical properties and reactivity.
In contrast, inorganic molecules often have simpler structures and fewer functional groups. They tend to be more stable and less reactive than organic molecules. The presence of functional groups in organic molecules makes them more susceptible to attack by other molecules, leading to higher reactivity.
The reactivity of organic molecules is essential for life. It allows for the formation and breakdown of complex molecules, which is crucial for biological processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. The reactivity of organic molecules is also harnessed in various industrial applications, such as the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and fuels.
Understanding the reactivity of organic molecules is therefore important for fields such as chemistry, biology, and medicine. By studying the reactivity of organic molecules, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms of chemical reactions and develop new molecules with desired properties.
Solubility
This aspect of concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas is significant because solubility governs the ability of molecules to dissolve in water, which is a crucial factor in many chemical and biological processes. The solubility of organic molecules in water is influenced by their polarity and the presence of functional groups.
- Polarity and Solubility
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrical charge within a molecule. Inorganic molecules, such as sodium chloride (NaCl), tend to be ionic and highly polar. This polarity allows them to dissolve readily in water, which is also a polar solvent. In contrast, organic molecules, such as hydrocarbons, are typically nonpolar or weakly polar. Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve well in water because they do not interact strongly with the polar water molecules.
- Functional Groups and Solubility
The presence of functional groups in organic molecules can also affect their solubility in water. Functional groups, such as hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH), are polar and can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This can increase the solubility of organic molecules in water. However, the presence of nonpolar functional groups, such as alkyl (-CH3) and aryl (-C6H5), can decrease solubility in water.
- Implications for Biological Processes
The solubility of organic molecules in water has important implications for biological processes. Many biological processes, such as metabolism and transport, occur in aqueous environments. The solubility of organic molecules in water determines their ability to participate in these processes and interact with other molecules in the body.
In summary, the solubility of organic molecules in water is influenced by their polarity and the presence of functional groups. This aspect of concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas is important for understanding the behavior of organic molecules in biological and chemical systems.
Occurrence
This aspect of "concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas" highlights the fundamental distinction between organic and inorganic molecules based on their presence in living organisms.
- Facet 1: The Prevalence of Organic Molecules in Life
Organic molecules are the building blocks of life. They form the of all living organisms, from the simplest bacteria to complex multicellular animals and plants. Organic molecules include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for cellular structure, metabolism, and genetic information storage.
- Facet 2: The Ubiquity of Inorganic Molecules
Inorganic molecules are found not only in living organisms but also in non-living matter. They include water, minerals, gases, and salts. Water is crucial for life and about 60% of the human body. Minerals provide essential nutrients for organisms, while gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide are involved in respiration and photosynthesis.
- Facet 3: The Interplay of Organic and Inorganic Molecules
Organic and inorganic molecules often interact and cooperate within living organisms. For example, enzymes, which are proteins (organic molecules), require inorganic cofactors such as metal ions to function. The interplay between organic and inorganic molecules is essential for maintaining homeostasis and carrying out biological processes.
In summary, the occurrence of organic molecules in all living things and the presence of inorganic molecules in both living and non-living things is a fundamental aspect of "concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas." This distinction highlights the unique role of organic molecules in life and the diverse functions of inorganic molecules in both biological and non-biological systems.
Importance
Understanding the importance of organic and inorganic molecules is crucial within the concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas. Organic molecules are the foundation of life, while inorganic molecules play a vital role in shaping and sustaining the environment. Exploring their significance unveils their interconnectedness and the delicate balance they maintain within our world.
- Facet 1: The Pillars of Life
Organic molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. They provide energy, structure, and genetic information necessary for life's processes. Without organic molecules, life as we know it would cease to exist.
- Facet 2: The Environmental Guardians
Inorganic molecules, such as water, carbon dioxide, and minerals, are essential components of the environment. Water is the lifeblood of our planet, supporting all living organisms. Carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Minerals provide essential nutrients for plant and animal life.
- Facet 3: Interdependence and Balance
Organic and inorganic molecules are not isolated entities; they interact and depend on each other within ecosystems. For instance, plants, composed primarily of organic molecules, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen, an inorganic molecule vital for animal respiration. This delicate balance ensures the sustainability of life on Earth.
In summary, the importance of organic molecules for life and inorganic molecules for the environment highlights their profound roles in the concepto de moleculas organicas e inorganicas. Their interconnectedness and interdependence demonstrate the intricate harmony that governs our planet's ecosystems. Understanding these concepts is vital for appreciating the delicate balance of nature and the profound impact of both organic and inorganic molecules on our world.
FAQs on Concepto de Moleculas Organicas e Inorganicas
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the concept of organic and inorganic molecules, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the fundamental difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Organic molecules are characterized by the presence of carbon, while inorganic molecules lack carbon in their composition. This distinction forms the basis for their unique properties and functions.
Question 2: Are all organic molecules naturally occurring?
While many organic molecules are found in nature, synthetic organic molecules can also be created in laboratories. Organic synthesis allows chemists to design and produce complex organic compounds for various applications.
Question 3: Can inorganic molecules be found in living organisms?
Yes, inorganic molecules play crucial roles in living organisms. Water, for example, is essential for all life forms, and minerals provide necessary nutrients and cofactors for biological processes.
Question 4: Are organic molecules always more complex than inorganic molecules?
Not necessarily. Some inorganic molecules, such as minerals, can have complex structures and compositions. However, organic molecules generally exhibit a wider range of structural diversity and complexity.
Question 5: How do organic and inorganic molecules interact in biological systems?
Organic and inorganic molecules often interact and cooperate within living organisms. For instance, enzymes, which are proteins (organic molecules), require inorganic cofactors (inorganic molecules) for their catalytic activity.
Question 6: What are the key applications of organic and inorganic molecules?
Organic molecules form the basis of pharmaceuticals, plastics, fuels, and many other products. Inorganic molecules find applications in electronics, construction, agriculture, and various industrial processes.
In summary, understanding the differences and significance of organic and inorganic molecules is essential for comprehending their roles in life, the environment, and technological applications.
Transition to the next article section:
Conclusin
El concepto de molculas orgnicas e inorgnicas es fundamental para comprender la qumica de la vida y el mundo que nos rodea. Las molculas orgnicas, caracterizadas por la presencia de carbono, son los bloques de construccin de todos los seres vivos, mientras que las molculas inorgnicas, sin carbono, desempean funciones cruciales en el medio ambiente y en los procesos biolgicos.
La distincin entre molculas orgnicas e inorgnicas se extiende ms all de su composicin, abarcando sus propiedades, reactividad y solubilidad. El estudio de estas molculas ha llevado a avances en medicina, biologa, qumica y otros campos, mejorando nuestra comprensin del mundo natural y allanando el camino para nuevas tecnologas.
Al comprender el concepto de molculas orgnicas e inorgnicas, podemos apreciar la intrincada danza de la vida y la materia, y reconocer la importancia de estas molculas en nuestro planeta y ms all.
Find State-Accredited Law Schools In California: A Comprehensive Guide
The Ultimate Guide To First-Party Cookies: Understanding The Basics
The Ultimate Guide To Avoiding Costly Bearings Failure

Qué son las biomoléculas y cómo se clasifican Educación Activa

MOLÉCULAS ORGÁNICAS 54 jugadas Quizizz
Química y Algo Más! Las Biomoléculas y el ADN